**Summary of Investigation and Analysis of Building Deformation Joints**
Buildings are subject to various external forces such as temperature fluctuations, loads, and seismic activities, which can cause deformation, cracking, and structural damage. To prevent such issues, it is essential to incorporate deformation joints in key areas of the structure. During our investigation, we not only focused on deformation joints but also examined other structural components of the building, gaining practical insights that complemented our textbook knowledge. This field study helped us understand the importance of proper design and construction in real-world scenarios.
**Keywords**: Deformation joint; Structural requirements; Construction; Practice
Deformation joints are critical elements in building design, allowing different sections of a structure to move independently without causing damage. These joints are strategically placed to accommodate expansion, settlement, or seismic movements. By breaking the building into independent units or simpler sections, the joints help maintain structural integrity while allowing for necessary movement.
Based on their purpose, deformation joints can be classified into three main types: expansion joints (temperature joints), settlement joints, and seismic (anti-vibration) joints.
**2.1 Expansion Joints**
Expansion joints are designed to handle thermal expansion and contraction. They are typically installed when the building's length exceeds certain limits, depending on the structure type and roof insulation.
- **Setting Conditions**: Based on building length, structure type, roof rigidity, and insulation status.
- **Construction Requirements**: The foundation may or may not be disconnected, but the structure must be separated from the foundation up to the roof.
- **Slit Width**: Generally between 20–30 mm.
**2.2 Settlement Joints**
These joints are used to prevent damage caused by uneven foundation settlement. They divide the building into separate structural units that can settle independently.
- **Setting Conditions**: When the building has a complex shape, large height differences, significant load variations, or different foundation types.
- **Construction Requirements**: All parts of the building must be disconnected from the foundation to the roof.
- **Joint Width**: Typically 30–70 mm for general foundations, and wider for collapsible loess foundations.
**2.3 Seismic Joints**
Seismic joints are essential in earthquake-prone areas. They help reduce stress concentrations during earthquakes by dividing the building into smaller, more rigid segments.
- **Setting Conditions**: When there are large protrusions, height differences exceeding 6 meters, or significant variations in structural stiffness or mass.
- **Construction Requirements**: The foundation should be disconnected, and walls or columns should be provided on both sides of the joint for added stability.
- **Joint Width**: For multi-story buildings, the minimum width depends on height and seismic intensity. For example, up to 15m, 70mm is sufficient; beyond that, the width increases with height and seismic level. Frame-shear wall structures use 50% of these values, but not less than 70mm.
By understanding the role and application of deformation joints, we gained a deeper appreciation of how architectural design and engineering principles work together to ensure safety, durability, and functionality in modern buildings.
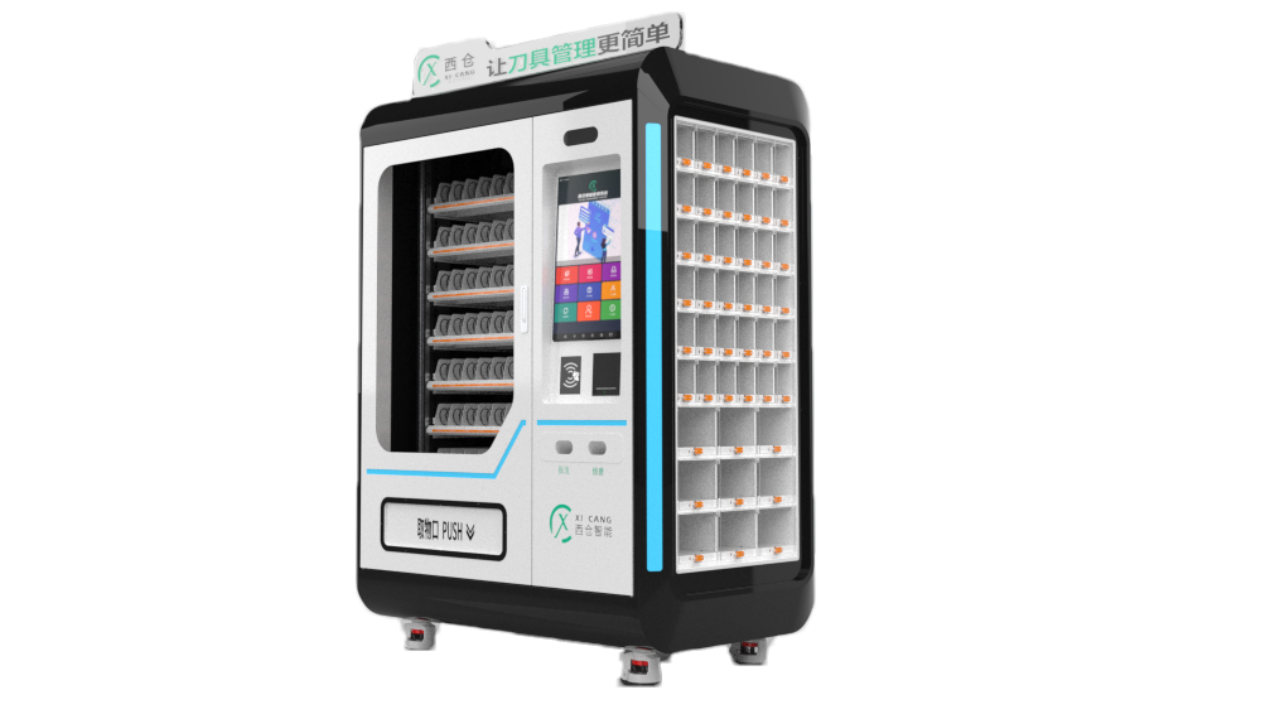
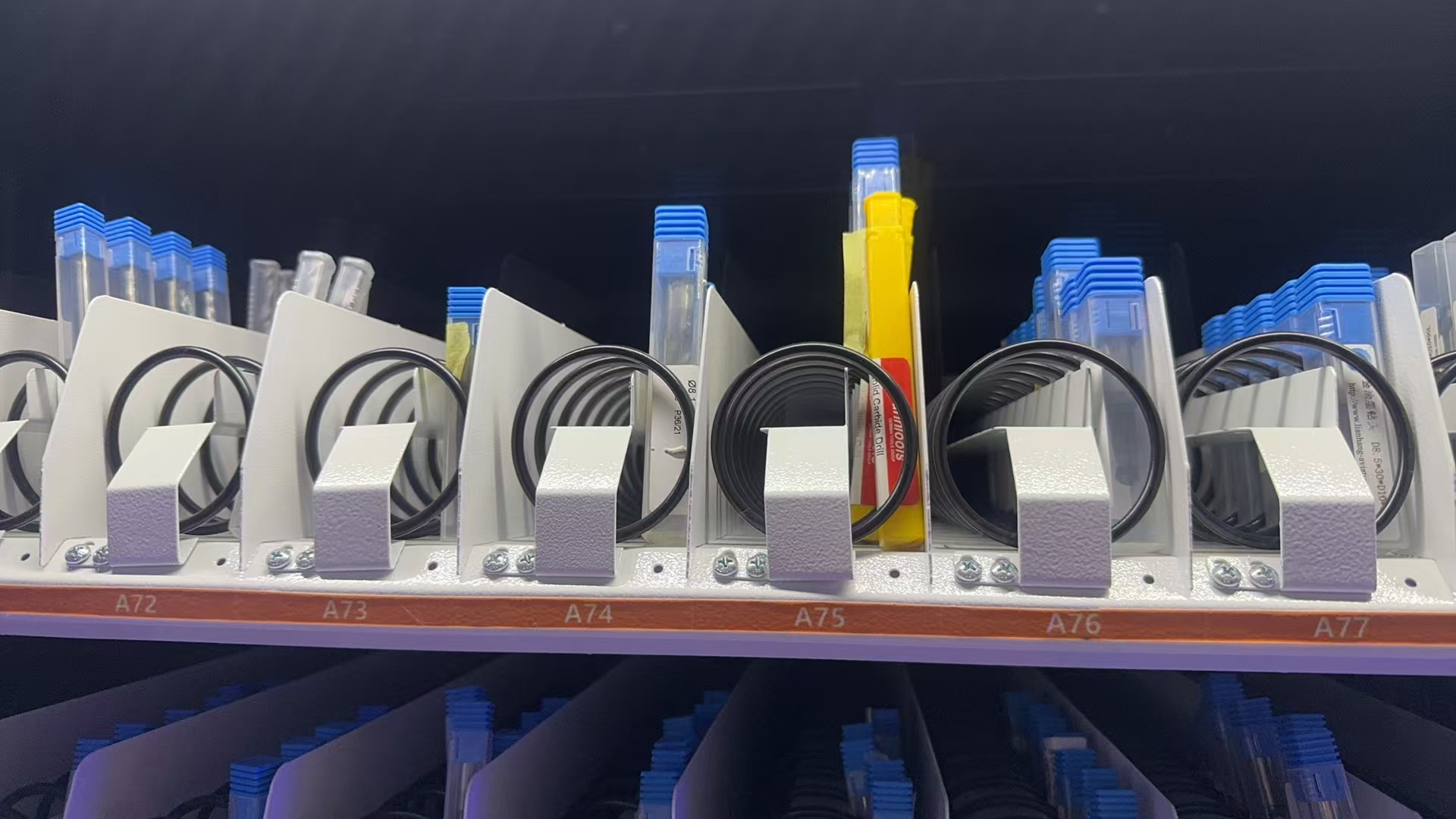
Spring Coil Cabinets
Spring Coil Cabinets
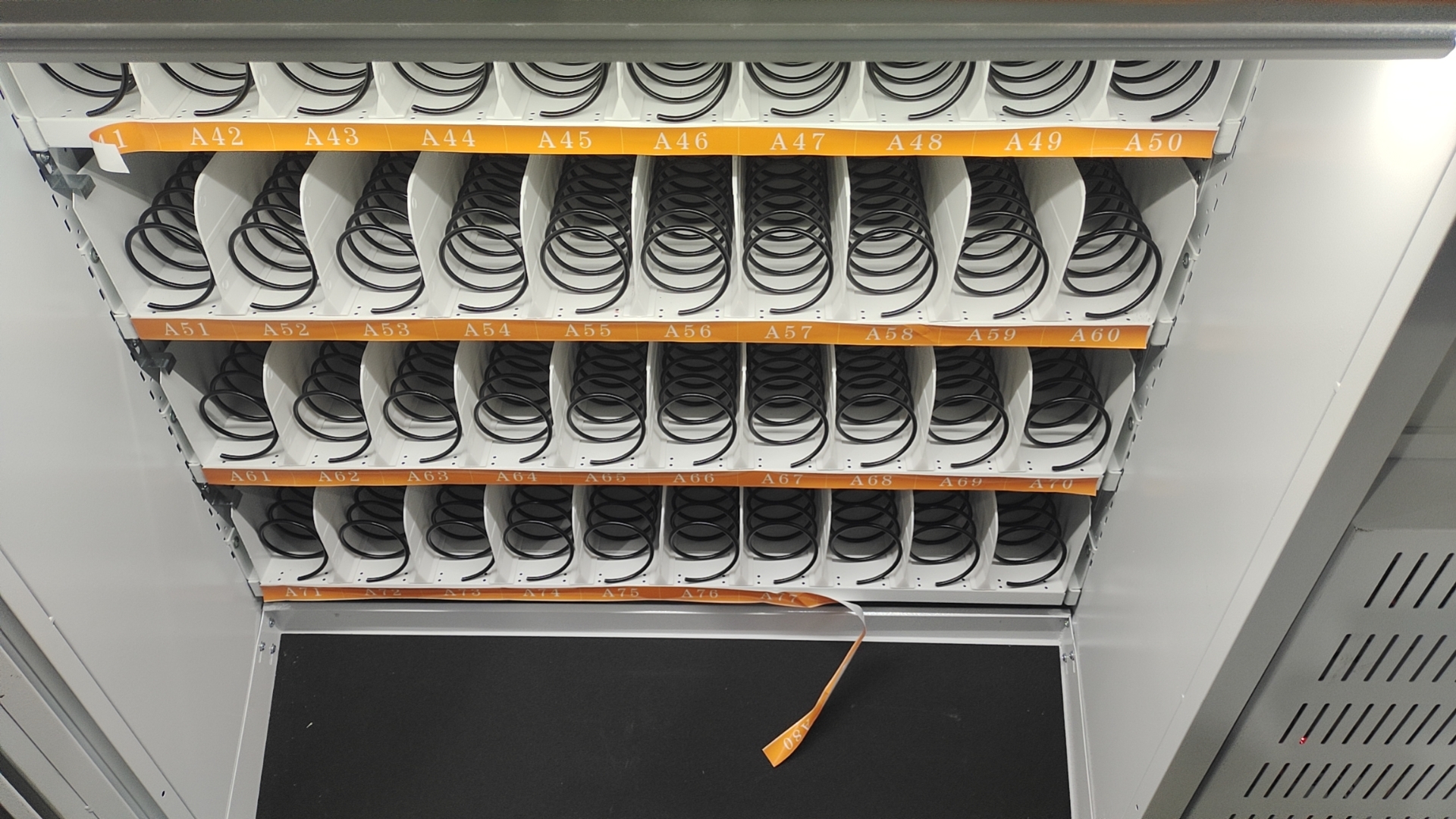
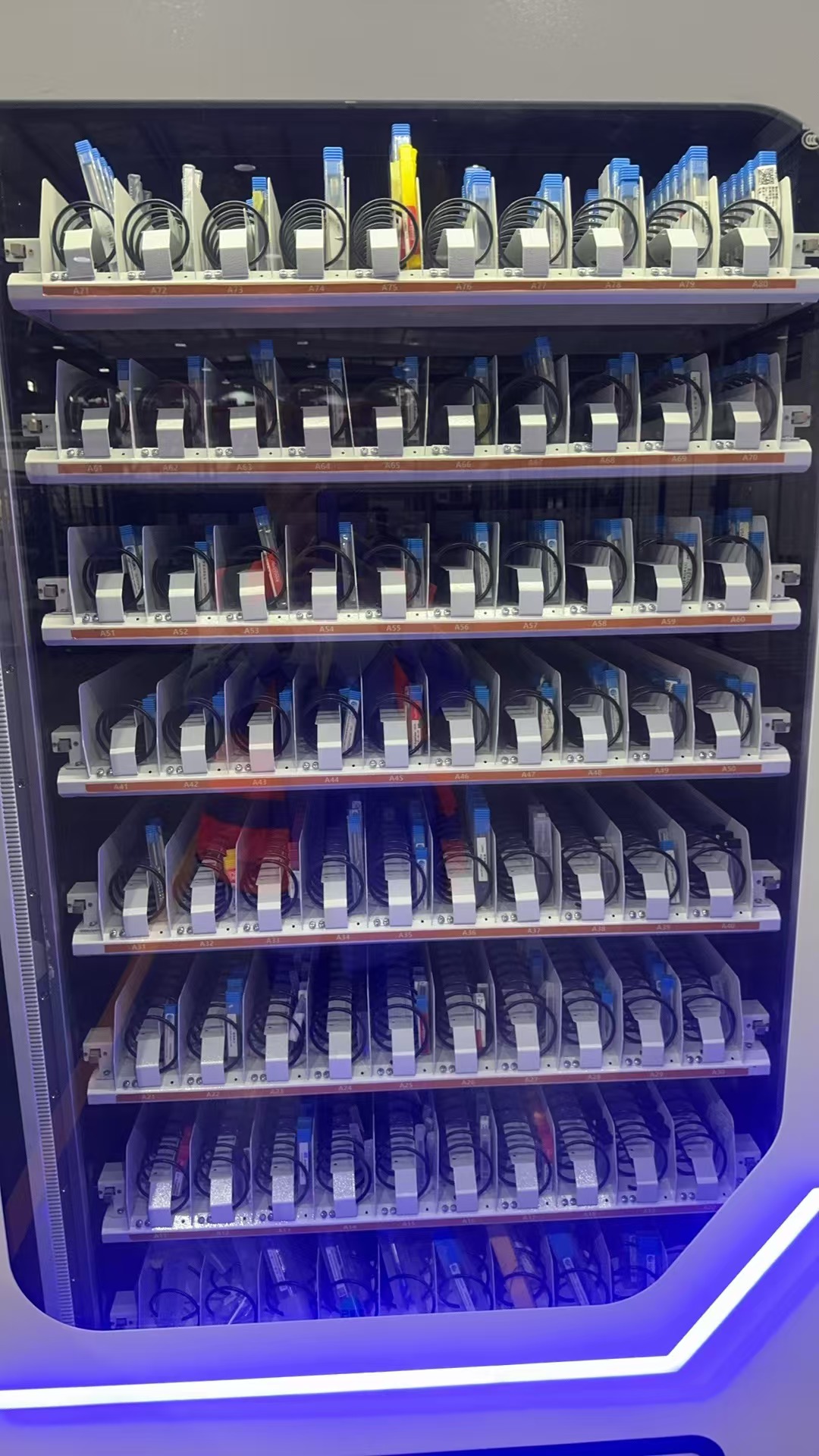
Ideal for dispensing boxed or small packaged items such as cutting tools, gloves, or inserts.
This smart cabinet integrates spring coils and grid compartments with a vertical lifting platform, designed to store and manage various boxed tools, inserts, gloves, and small components. The lift system automatically brings the selected tray to the access window, making it easy and ergonomic for users to retrieve items.
The cabinet supports user authentication (RFID, code, face), real-time inventory tracking, and automatic refill reminders. With flexible configurations and a compact footprint, it’s ideal for tool rooms, CNC workshops, and production lines.
Applications:
CNC tool storage, consumable management, workshop automation, tool distributors.
Features:
Compact design, mixed storage modes, lifting platform, smart access control, customizable layout.
Intelligent Cnc Tool Storage Cabinet,Wooden Drawer Cabinet,Intelligent Equipment Management Cabinets
Jiangsu Xicang Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.xciwarehousing.com