I. Overview
In industrial production, threaded joints are widely used in various parts of mechanical equipment. The threaded joint can maintain high precision, can generate large axial force, can realize self-locking, and at the same time realize large-scale standardized production. Therefore, its processing cost is low and interchangeability is good, and it is also used in the modern automobile industry. A wide range of applications. According to statistics, there are about 500 kinds of fasteners applied to a car.
Since the breakage of the bolt is sudden and easy to find; and the tripping of the thread is gradually occurring, it is difficult to find and increase the risk of accident caused by the failure of the fastener. Therefore, the design of the threaded connection, It is always desirable that the failure mode is a bolt break, rather than a thread trip. When designing threaded joints, the standard bolts and nut assemblies and the matching requirements of the bolts and nuts in the standard can be used without regard to the thread tripping of the bolts and nuts. However, if bolts are screwed into the internal thread parts, Thread material and strength difference, in order to ensure that the thread of the bolt and nut will not trip, the thread must be calculated, that is, the minimum mesh length of the thread is calculated.
At present, the design of threaded holes in domestic design data is very general. There is no classification of different bolt strength grades and material strengths, which is not conducive to accurate design. For example, the design requirements for threaded hole depth are: steel or bronze material threaded hole meshing length H The nominal diameter of the thread is d; the cast iron material H is about (1.25~1.5) d; the aluminum alloy material H is about (1.5~2.5)d. Therefore, it is necessary to analyze the calculation method of the minimum meshing length of the thread to ensure the rationality and accuracy of the design. According to the research comparison, there are three main methods for calculating the current thread engagement length:
1. The calculation method of the minimum meshing length of the thread in the VDI2230-1 standard;
2. Calculation method of thread strength in mechanical design;
3. Calculation method of thread limit rotation length in theory and calculation of threaded joint
This paper mainly introduces the calculation method of these 3 in detail, and compares with the examples to determine the appropriate calculation method for the minimum meshing length of the thread.
1. Calculation method of minimum meshing length of thread in VDI2230-1 standard
The VDI2230 standard is a specification for high-strength bolt design calculations compiled by the German Society of Engineers. It covers all the steps of bolt design calculation and has become a system for bolt design calculation, which is adopted by major automakers in the automotive industry. The latest standard consists of two parts: VDI2230-1-2015 single cylinder bolt design calculation; VDI2230-2-2014 bolt group load force calculation. The calculation method of the minimum meshing length of the threaded connection is introduced in detail in VDI2230-1-2015. The calculation method refers to the research results of the paper "Analysis and Design of Thread Assembly", and the appendix of ISO898-2 standard also studies the same. The results show that the height design of the standard nut is calculated based on the research results. Therefore, it is very suitable to calculate the minimum mesh length of the thread using the VDI2230-1 standard, and the accuracy can be ensured.
Due to the influence of the 60° thread wedge factor, the nut will expand under the load, which will increase the diameter of the nut and reduce the effective shearing area of ​​the inner and outer threads. This expansion will be more pronounced as the wall thickness of the nut or the ratio s/d of the opposite side dimension to the nominal diameter decreases. For bolts and nuts, the thread strength reduction factor C1 due to nut expansion is:
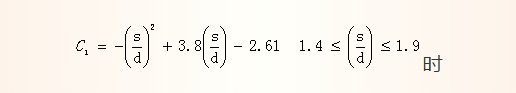 Time
Time For the design of the internally threaded hole, the distance of the internal thread axis to the edge of the connected member is e=d+(3~6)mm, that is, s/d>2, and C1 is calculated according to 1.0. The curve of the thread strength reduction coefficient C1 with s/d due to the expansion of the nut is shown in Fig. 1.
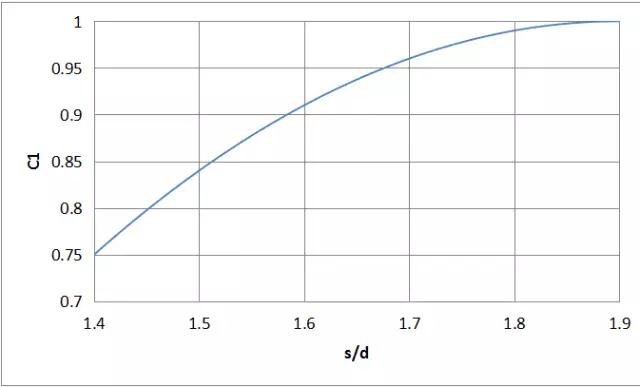
Fig.1 Curve of the thread strength reduction coefficient C1 caused by nut expansion with s/d
When the bolts and nuts are subjected to loads, the threads of the bolts and nuts will be elastically deformed. Once the load is large enough, the threads will be plastically deformed or bent. This bending of the thread reduces the effective shear area of ​​the thread and, at the same time, causes the nut to expand more. Therefore, when calculating the shear strength of the thread, it is necessary to consider the influence coefficient C2 and C3 of the bending of the bolt and the nut thread, and the influence coefficient of the thread bending is as shown in Fig. 2.


Fig. 2 Curve of bending influence coefficient with intensity ratio Rs
According to the curve of the bending influence coefficient with the intensity ratio Rs, it can be seen that when Rs is lower, C3 exceeds 1, the main reason is that the nut strength is low, and when the bolt strength is high, the nut thread is higher in the stronger thread. The bending deformation is not easy to occur inside, and the shear strength of the nut thread is increased. This is in line with the content of the GB/T 3098.2 standard "the use of hardened core rods requires a higher tripping strength than the bolts of the corresponding performance grades".
The influence coefficient is related to the strength ratio Rs of the bolt and the nut, and the Rs is related to the tensile strength RmM, RmS of the nut and the bolt, and the thread shearing area ASGM and ASGS of the nut and the bolt, as shown in the following formula.

When the external thread is released, the thread will be sheared along the cylindrical surface formed by the small diameter of the nut thread; when the internal thread is released, the thread will be sheared along the cylindrical surface formed by the large diameter of the bolt, as shown in Fig. 3. Therefore, the shear areas ASGM and ASGS of the nut and bolt threads are:
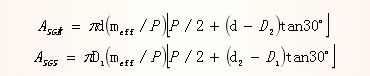
Where: P is the pitch, D1 is the internal thread diameter, D2 is the internal diameter of the internal thread, and the diameter of the external thread of d2
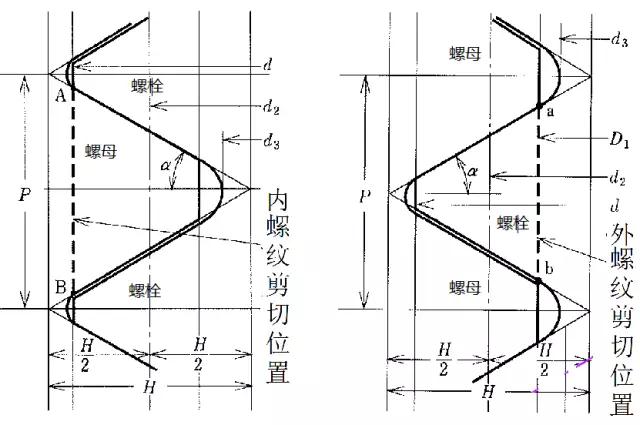
Figure 3 Schematic diagram of internal and external thread cutting position
When the thread does not trip, the thread of the bolt and nut must be able to withstand the maximum preload force that can be achieved when the bolt is tightened. In the automotive industry, in order to reduce the weight and make full use of the material of the bolt, the bolt tightening is often carried out by means of torque-rotation and yielding. The pre-tightening force of the bolt is high. Therefore, the highest pre-tightening force of the bolt can be achieved according to the maximum resistance that the bolt can reach. The tensile strength Rmmax is calculated. The maximum tensile strength Rmmax of the bolt is usually 1.2 times the minimum tensile strength Rmmin of the bolt, that is, Rmmax=1.2Rmmin.
In order to ensure the safety and uniformity of the calculation results, only the axial force of the bolt is calculated when the bolt is tightened, and the torsional shear stress is not considered. For the internal thread, when the large diameter d of the thread reaches the lower limit of the tolerance, the median diameter D2 of the nut thread reaches the upper limit of the tolerance. This is the most unfavorable condition for the load of the internally threaded connector. The minimum meshing length required for the nut is:
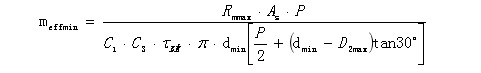
For the external thread, when the middle diameter d2 of the bolt thread reaches the lower limit of the tolerance, the nut thread diameter D1 reaches the upper limit of the tolerance. At this time, the load of the externally threaded connecting member is the most unfavorable. The minimum meshing length required for the bolt is:
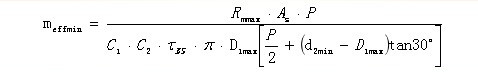
Ï„BM is the minimum shear strength of the internal thread material, and Ï„BS is the minimum shear strength of the bolt material. The shear strength of different materials has a certain proportional relationship with the tensile strength. For details, refer to the VDI2230-1 standard. According to the above calculation of the minimum meshing length of the thread required for the nut and bolt, take the maximum value of the two to obtain the minimum meshing length of the bolt and nut connection. It can be seen from the calculation process that the calculation method of VDI2230-1 thread engagement length is calculated according to the thread shear strength. At the same time, the influence coefficient of nut expansion and thread bending is considered in the calculation.
When the height of the nut or internal thread is designed, the height of the chamfer should be increased based on the minimum meshing length of the thread.
Second, the calculation method of thread strength in mechanical design
In the calculation, a circle of thread is unfolded along the large diameter of the nut or the small diameter of the bolt, and the thread is regarded as a cantilever beam model. The force of the thread is applied to the middle diameter of the thread. According to the calculation method of the shear strength and bending strength of the material mechanics, it can be concluded that the minimum meshing length of the thread is meffmin:
External thread shear strength conditions:

Internal thread shear strength conditions:
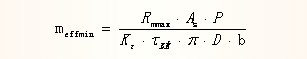
External thread bending strength conditions:
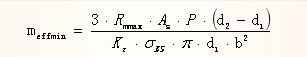
Internal thread bending strength conditions:
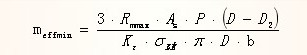
Where: d1 is the external thread diameter
Kε unevenness coefficient of each thread
b is the width of the thread root (for normal thread b = 0.87P)
σBS is the bending strength of externally threaded parts
σBM is the bending strength of internally threaded parts
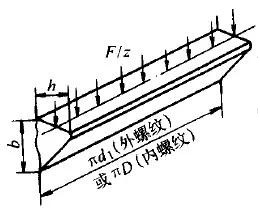
Figure 4 Schematic diagram of the force of the internal and external threaded teeth
The calculation method is calculated according to the calculation theory of the cantilever beam according to the development of one thread. The shear strength and bending strength of the thread are considered in the calculation. When the actual thread is engaged, there will be multiple threads engaged with each Other, and the gap between the internal and external threads is better. Small, does not produce a large bending, therefore, the bending strength and the actual difference are considered for the threaded connection.
Third, the theory and calculation of the thread connection calculation method of the thread limit rotation length
"Theory and Calculation of Threaded Connections", Dr. Yamamoto, Japan, combined with the latest research results of G. Junker, compiled a book on the calculation of the thread strength calculation, which details the calculation method of the thread limit rotation length. Calculate the thread shear failure according to the actual test of internal and external threads, and derive the calculation formula of the thread's limit screw length by theoretical method. The internal and external thread shearing diagram is shown in Fig. 5.
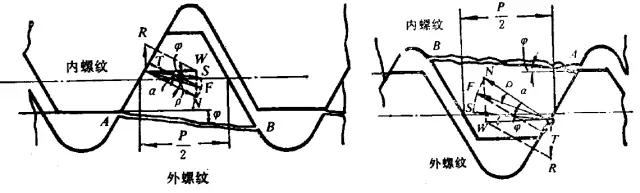
Figure 5 Schematic diagram of internal and external thread cutting
Minimum meshing length of external thread:
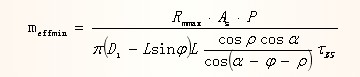
among them
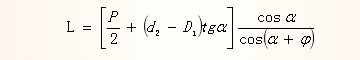
In the formula:
а is the half angle of the tooth type, the normal metric thread is 30°
φ is the angle between the thread shear line and the thread axis, the external thread φ is 18°, and the internal thread φ is 0°.
Ï is the friction angle of the thread surface, and when the friction coefficient of the thread surface is μth, Ï=arctgμth
Minimum threading length of internal thread:
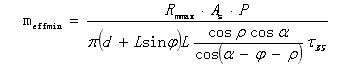
among them

Fourth, the calculation example
For the bolt M12×1.5-10.9 screwed into the internal threaded hole of the internal thread material QT500-8, the minimum tensile strength Rmmin of the female threaded hole is 500MPa, the internal thread shear strength is 450MPa, and the internal thread bending strength is 600MPa. The minimum tensile strength of the bolt is 1040MPa, and the maximum tensile strength is 1190MPa. The minimum meshing length of the thread calculated by three different calculation methods is shown in Table 1.
Table 1 M12 × 1.5 thread minimum mesh length
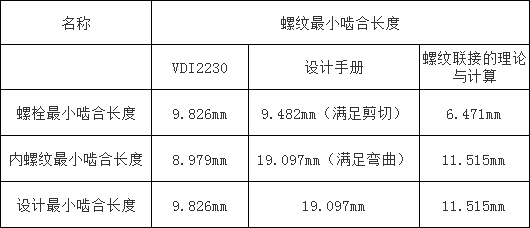
It can be seen that there is a big difference in the minimum meshing length of the three threads. The calculation method of the design manual considers the bending strength of the thread, and the minimum required meshing length is 19.097 mm, which is much larger than the calculation results of the other two methods. If only the shear strength of the thread is considered, the design manual calculation method yields a minimum mesh length of 11.369 mm, which is similar to the calculation results of the other two methods. The difference between the minimum meshing lengths obtained by the VDI2230 and the threaded joint theory and calculation is small, and both are calculated according to the shear strength of the thread. Because the height of the nut in the ISO898-2 nut standard is calculated according to the research results of Alexander, EM: Analysis and design of threaded assemblies, and the VDI2230-1 standard is also the reference of the research results. At the same time, the standard is the threaded connector. A calculation system, therefore, the calculation of the minimum mesh length of the thread should use the calculation method of VDI2230-1.
V. Conclusion
The calculation method in the design manual is calculated according to the theory of the cantilever beam according to the rotation of one circle. The shear strength and bending strength of the thread are considered in the calculation, but the actual thread is multi-turn meshing, and the internal and external thread clearance is small, it is difficult to produce a large The bending deformation is mainly based on the shearing of the thread. Therefore, the minimum meshing length of the thread is calculated according to the design manual, and only the shearing of the thread can be calculated. This can also be seen from the calculation example. If the bending strength of the thread is taken into account, the minimum meshing length of the thread will be quite different from other calculation methods, which is inconsistent with the actual.
Both the theory and calculation of VDI2230-1 and threaded joints only consider the shearing of the thread, which meets the meshing requirements of the actual thread, and the calculation results are also small. Considering that VDI2230-1 is a calculation system standard for threaded joints, the actual calculation of thread engagement length is based on the calculation method of VDI2230-1 standard.
kaiping aida sanitary ware technology co.,ltd , https://www.kpfaucets.com